UTAH SHIPS

USS Salt Lake City at Wake Island, 1942
United States Navy ships are named using rules established by law, custom, and tradition. They may honor states, cities, counties, distinguished people and geographical locations. The following ships were named for the State of Utah, for cities, counties, geographical locations in Utah, and Utahns who served this country with distinction.
USS Bennion (DD 662): The Bennion was named for Mervyn Sharp Bennion who was born in Vernon, Utah, 5 May 1887 he graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy in 1910. As commanding officer of the battleship West Virginia, Captain Bennion was killed in action at Pearl Harbor on 7 December 1941. He was posthumously awarded the Medal of Honor.
The Bennion, a Navy destroyer, was commissioned on 14 December 1943 and saw extensive action in the Pacific during World War II. She was decommissioned on 20 June 1946.
USS Robert Brazier (DE 345): Robert Brazier was born in Tooele, Utah. He joined the Navy in 1939 and was killed in action 4 June 1942 during the battle of Midway. He was posthumously awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross.
The Robert Brazier, a destroyer escort, was commissioned on 18 May 1944 and performed escort duty for various convoys in the South Pacific until the end of World II. She was decommissioned on 16 September 1946 and used as a target vessel.
USS BRYCE CANYON (AD 36): The Bryce Canyon, a destroyer tender, was named for the National Park in Utah. Commissioned on 15 September 1950, with the mission of providing repair services to destroyers and other combatant ships, she was scrapped on 30 June 1981.
USS Daggett County (LST 689): There is no history for the Daggett County currently available. She would have survived World War II since LSTs (Landing Ship Tanks) were not named during the war but served by hull number designation only, for example, LST-689. It was not until 1955 that LSTs were named for state counties.
USS Escalante (AO 70): The Escalante was commissioned in 1943 and named for the river in Utah. Originally a merchant oiler, she was acquired by the Navy for combat duty during World War II and assigned to the Atlantic Fleet. Prior to the Normandy invasion she was transferred to the Pacific Fleet and participated in action against Luzon, Iwo Jima, Okinawa, and mainland Japan. The Escalante was decommissioned 12 December 1945 and transferred to the Maritime Commission.
USS Escalante River (LSMR 502): LSMRs were medium landing ships converted to fire support ships armed with guns and rocket launchers. There is no history available for the USS Escalante River; however, she was most likely a sister ship to the Grand River and Green River.
USS Garfield County (LST 784): The Garfield County was commissioned on 1 September 1944 and participated in the island invasions of Tinian and Okinawa. She was decommissioned in March 1946.
USS GRAND RIVER (LSMR 505): The Grand River was commissioned on 14 June 1945 and joined the Pacific Fleet a few days before the Japanese surrender. She was decommissioned after eleven months service and placed in the Reserve Fleet.
USS GREEN RIVER (LSMR 506): The Green River was a sister ship to the Grand River. Commissioned on 19 June 1945 she was decommissioned after eleven months service and placed in the Reserve Fleet.
USS Iron County (LST 840): Commissioned 11 December 1944, the Iron County participated in the assault on Okinawa and the occupation of Japan. She was decommissioned on 1 June 1946. Recommissioned during the Korean conflict, she operated between Korea and Japan. She also assisted the French in Indochina during 1954. In 1 July 1958 the Iron County was transferred to the Republic of China (Taiwan) and renamed Chung Fu.
USS Kane County (LST 853): The USS Kane County was commissioned on 11 December 1944 and joined the Pacific Fleet. She was decommissioned in 1946 and transferred to the Republic of Korea in 1958, serving as the Su Young.
USS Merrill (DE 392): Howard Deel Merrill was born 16 December 1917 in Provo, Utah. He graduated from the Naval Academy in 1940 and reported to his first duty station, the USS Arizona, where he was killed on 7 December 1941 as a result of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. The USS Merrill was commissioned on 17 November 1943 and performed escort duty for fifteen convoy crossings of the Atlantic. Transferred to the Pacific Fleet, she was en route to Pearl Harbor when World War II ended. Soon afterward she was decommissioned and transferred to the Atlantic Reserve Fleet.
USS Millard County (LST 987): The Millard County was
commissioned on 19 April 1944 and spent her first year of service as an
Atlantic Fleet training ship. In 1945 she was transferred to the Pacific
Fleet, operating in the South Pacific and Japanese waters in support of
the occupation of Japan. The Millard County was decommissioned in
1946 and sold to the West German Navy in 1961.
USS Morgan County (LST 1048): The Morgan County was
commissioned on 28 March 1945. She operated in the Marshall Islands in support
of various base establishments by the Third Marine Division. The Morgan
County was turned over to the Army after World War II ended and assisted
in the occupation of Japan.
During the Korean conflict she was given back to the Navy for service along the Korean coast. She participated in the invasion of Inchon and was subsequently decommissioned on 10 May 1956.
USS Navajo: The name Navajo has been given to four different ships in honor of the Indian tribe residing in the States of Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico. Three of these ships were ocean going tugs. The first was commissioned in 1907, assigned to Pearl Harbor, and decommissioned in 1924. The second (AT 64) saw service in World War II in the South Pacific and was sunk due to enemy action. The third Navajo (ATA 211) was commissioned in 1945, serving between San Diego and Pearl Harbor, and was decommissioned in 1962. The other Navajo was a motor patrol boat (SP298), commissioned in 1917, that spent her entire career on the east coast patrolling harbor entrances and submarine nets during World War I. She was decommissioned and sold on 1 November 1919.
USS Melvin R. Nawman (DE 416): Melvin Nawman was a graduate of the University of Utah. He was commissioned a Second Lieutenant in the Marine Corps seeing action as a pilot during the struggle for Guadalcanal. He died three days after the initial Guadalcanal assault, on a volunteer mission, attempting to stop the Japanese from landing additional reinforcements.
The Nawman was commissioned on 16 May 1944 and assigned destroyer escort duties during the Marshall Island invasion. Decommissioned after the war she was recommissioned during the Korean conflict to serve as a training ship for midshipman. USS Nawman was decommissioned a second time in August 1960.
USS Ogden (PF 39): One of two ships named for the city of Ogden, Utah. The Ogden (PF 39) was commissioned on 10 December 1943. Her primary mission, as a patrol frigate, was to escort convoys during the latter years of World War II. The Ogden was decommission in July 1945 and transferred to the Russian Navy under the lend-lease program. She was returned to the United States and then given to the Japanese in January 1953 to serve as the Kusu.
USS Ogden (LPD 5): An all-purpose amphibious warfare ship combining the functions of an attack transport and attack cargo ship, the second Ogden is classified as an Amphibious Transport Dock. Commissioned on June 1964, she served during the Vietnam conflict and is still on duty.
USS PAIUTE (ATF 159): Named for the Paiute Indian tribe of southwestern Utah, she was commissioned 17 August 1945. Her major duties included salvage, towing and logistics throughout the North Atlantic. The Paiute participated in the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962 and in the Dominican Republic in 1965. She was also used in the recovery of Gemini 6 and 7 and Apollo 7 and 9 spacecraft. The Paiute was transferred to the Naval Reserve Force 1 February 1977.
USS Provo (AG 173): Named for the city of Provo, Utah, she was a special projects ship built in 1945 by the Maritime Administration as the Drew Victory. She was later renamed California and Utah during her civilian career until she was acquired by the Navy in 1963 and renamed Provo. During the 1970s the Provo was a point to point cargo carrier delivering cargo to Okinawa and Vietnam.
The Provo Victory (AK 228): The "Victory" was added to many commercial ships acquired by the Navy during World War II. The Provo Victory was commissioned on 18 October 1944 and served in the South Pacific as a cargo carrier. On 10 April 1946 she was decommissioned and returned to the War Shipping Administration.
USS Richfield (AK 253): Originally named the Owensboro Victory, she delivered cargo and passengers to occupied Japan under the operation of Coastwise Lines, a commercial shipping company. Acquired by the Army and renamed the Private Joe E. Mann, she was returned to the Maritime Commission and then transferred to the Navy. Designated the USS Richfield in honor of the central Utah city, she was placed under the operation of the Military Sea Transportation Service as a cargo vessel. In 1968 she was transferred to the National Defense Reserve Fleet.
USS Salt Lake City (AC 25): One of two vessels named for Utah's capital city, this one, a heavy cruiser, was commissioned on 11 December 1929. During the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Salt Lake City was returning from Wake Island escorting the carrier Enterprise. In the months that followed, the Salt Lake City saw action off the Marcus and Santa Cruz Islands, the Solomons, the Aleutians, and other major campaigns in the South Pacific. At the close of World War II, the Salt Lake City was deactivated and used as a test vessel for the post-war atomic bomb tests. After surviving two atomic blasts, she was sunk as a target off the coast of southern California on 25 May 25 1948.
USS Salt Lake City (SSN 716): The second Naval vessel to honor this city was commissioned on 12 May 1984. As one of the Navy's newest nuclear powered submarines, her history is yet to be written.
USS Santaquin (YTB 824): Named for a chief of the Ute tribe, and a town in Utah, the Santaquin is a larger tug commissioned in 1973 and is still in service.
USS Sevier (APA 233): Named for the county in Utah, the Sevier was commissioned on 5 December 1944 as an Attack Personnel Transport ship tasked with delivering combat troops throughout the Pacific. She participated in the occupation of Japan and operation "Magic Carpet" bringing troops back to the United States. The Sevier was decommissioned on 30 April 1947.
USS Summit County (LST 1146): The Summit County was commissioned on 30 May 1945 and began her long career transporting construction supplies for the Seabees to various islands throughout the Pacific. After World War II ended the Summit County spent the next year delivery supplies to the Distant Early Warning (DEW) stations in Alaska. She also saw action during the Korean and Vietnam conflicts. After twenty years of service she was decommissioned.
USS Swenson (DD 729): Lyman Swenson was born in Pleasant Grove, Utah and graduated from the Naval Academy in 1916. He was killed onboard the USS Juneau during the battle for Guadalcanal.
The USS Swenson, a destroyer, was commissioned in 1944 and involved in battles at Formosa, Okinawa, and the islands of Japan. After World War II, she patrolled the waters off Korea participating in the Inchon landings and various shore bombardment missions. The Swenson saw duty during the Vietnam conflict and was decommissioned in 1969.
USS Tooele (PC 572): There is no history available for the patrol craft USS Tooele.
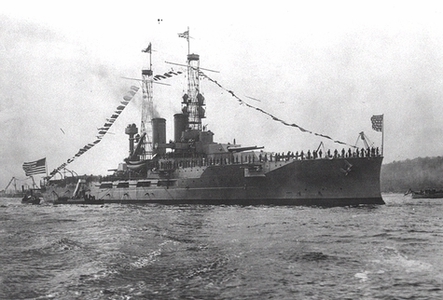
USS Utah
USS Utah (BB31/AG16): The battleship Utah was commissioned on 31 August 1911. During World War I she saw duty, primarily in Ireland, protecting convoy approaches to the British Isles. After World War I, battleship design progressed so rapidly that Utah became obsolete. She was one of a few battleships to survive after the Washington Treaty of 1922. This treaty placed total tonnage limitations on the signing countries. For the next nine years Utah served as the flagship for various naval squadrons and diplomatic missions.
The London Treaty of 1931 resulted in further naval limitations and Utah was redesignated as a target ship (AG 16). As the AG 16 she was outfitted with radio control devices which permitted control of the ship's engines and helm. The remote control of this giant ship was considered a major technological advance that, in a later generation, would be used in space operation at a latter time.
On Sunday, 7 December 1941, the Utah was moored at Pearl Harbor. She was torpedoed and sunk with the loss of six officers and fifty-two men. Her name was stricken from the list of Navy ships on 13 November 1944. She can still be seen at Pearl Harbor.
USS Ute (ATF 76): There is currently no history available for the seagoing tug USS Ute. She was named for the Ute Indian tribe and was transferred to the U.S. Coast Guard on 30 September 1980.
USS Wasatch (AGC 9): The Wasatch, named for the mountain range in Utah, was originally a merchant ship the SS Fleetwing. She was procured by the Navy Department and commissioned in 1944 as an amphibious force flagship. A communication nerve center for all amphibious assaults, she participated in the assaults on New Guinea, Borneo, and the Philippines. The Wasatch was decommissioned on 30 August 1946.
USS White River (LSMR 536): There is no history available for the USS White River.
Disclaimer: Information on this site was converted from a hard cover book published by University of Utah Press in 1994. Any errors should be directed towards the University of Utah Press.