Course Introduction
Course Introduction
Core Standards of the Course
Strand 1
Students will explore the fundamentals of fashion and associated careers.
Standard 1
Identify why we wear clothes
-
Protection - clothing that provides physical safeguards to the body, preventing harm from climate and environment.
-
Identification - clothing that establishes who someone is, what they do, or to which group(s) they belong.
-
Modesty - covering the body according to the code of decency established by society.
-
Status - establishing one's position or rank in relation to others.
-
Adornment - using individual wardrobe to add decoration or ornamentation.
Standard 2
Define common terminology.
-
Accessories - Articles added to complete or enhance an outfit. Shoes, belts, handbags, jewelry, etc.
-
Apparel - All men's, women's, and children's clothing.
-
Avant-garde - Wild and daring designs that are unconventional and startling. Usually disappear after a few years.
-
Classic - Item of clothing that satisfies a basic need and continues to be in fashion acceptance over an extended period of time. Timeless. (i.e. blazer, cardigan, denim, little black dress)
-
Design detail - The various garment parts that distinguish styles. Necklines, collars, sleeves, bodice, lapels, hemlines, etc. (a T-shirt is a garment type, the neckline changes the style of that garment. i.e. crew neck, Henley, V-neck, etc.)
- Shirts - T-shirt, polo, Henley, fitted, button-down
- Collars - Mandarin, notched, peter pan, button-down, shirt
- Sleeves - Set-in, raglan, dolman, leg-o-mutton, shirt cuff, French cuff
- Necklines - Scoop, crew, boat, sweetheart, cowl
- Dresses - Sheath, Shift, empire, dropped waist, shirtwaist, princess
- Skirts - Straight, A-line, yoke, gored, gathered, wrap
- Pants/trousers - flared/bootcut, straight, tapered
- Jackets/coats - blazer, double breasted, tuxedo, trench, bolero
-
Draped - Wrapped or hung on the body and usually held in place with pins, toggles, buttons, sash or belt.
-
Fad - A temporary, passing fashion. An item that has great appeal to many people for a short period of time. (silly bands, slap bracelets, etc.)
-
Fashion - The currently accepted style. A prevailing type of clothing that is favored by a large segment of the public.
-
Fashion cycle - A cycle of the rise, popularization, and decline of a particular style. Follows the sequence -introduction, rise, peak, decline, obsolescence.
-
Fit - The right size or how tight or loose the clothing is on the person wearing it.
-
Garment type - A category of clothing. Dress, coat, suit, sweater, pants, etc.
-
Haute Couture - (oat-koo-TOUR) The French term that literally means fine sewing. The finest clothing from fashion houses by major designers.
-
Ready to Wear - Clothing mass produced in standard sizes and sold to customers without custom alterations. (prêt-à poter)
-
Silhouette - The shape of a clothing style shown by its outer lines.
-
Style - A particular shape or type of apparel item. The style of a garment is determined by the distinct features that create its overall appearance. Specific design details create specific styles. (i.e. a sheath, shift and princess are all different styles of dresses)
-
Tailored - A garment made by cutting fabric pieces and then sewing them together to fit the body.
-
Trend - The movement of fashion into the through the marketplace. (Change in hemlines, waistlines, color, shoe style, etc.)
-
Wardrobe - All the apparel a person owns including all garments and accessories.
Standard 3
Discuss the history of fashion and how it is influenced by culture. (Lines between historical eras are fluid. The looks below are quintessential of that decade).
-
Trends repeat every 20-30 years
- 1890's - Victorian Era.
- Women - Gibson Girl (ideal American woman), corset, bustle, hourglass silhouette.
- Men - matching coat and vest with contrasting trousers. Rectangle silhouette.
- 1900's - Industrial Revolution Era.
- Women-pigeon breast shirtwaist, Leg O' Mutton sleeves, s-curve silhouette.
- Men - formal morning dress with top hats, or 3-piece 'lounge' suits with bowler hats. Rectangle silhouette.
- Both - Duster coat
- 1910's - WWI Era.
- Women - Hobble skirt, bathing suit, bloomers, inverted triangle silhouette.
- Men - military influence/trench coats. Rectangle silhouette
- 1920's - "Roaring '20's" Era.
- Women - Flapper, costume jewelry, cloche hat, dropped waistline, rectangle silhouette.
- Men - trousers creased with wider hemlines, introduction of the modern two-piece suit, zoot suit, wingtips. Hourglass silhouette.
- 1930's - Depression Era.
- Women - bias cut dresses, waistline restored, hemlinesdropped, handme-downs, flour sack clothing, Hollywood glamour, slight hourglass silhouette.
- Men - introduction of the double-breasted suit, padded shoulders, glen plaid fabric. Inverted triangle silhouette.
- 1940s - WWII Era.
- Women - Convertible suit (mix and match pieces), slacks, no silk ornylon stockings, inverted triangle silhouette.
- Men - Military influence/bomber jacket, austere "Victory" suits with no vest, cuff or pocket flaps. Rectangle silhouette.
- 1950s - Rock n' Roll era. Teenagers become their own class and have money to spend.
- Women - Poodle skirts, saddle shoes, Capri pants, the "New Look" (Christian Dior), hourglass silhouette.
- Men - dark flannel suits, the 'Ivy League' look - khaki slacks, button down shirt, sweater. Rectangle silhouette.
- 1960s - Civil rights Era.
- Women -Miniskirts, pantsuits, Chanel suit, pillbox hat, rectangle silhouette.
- Men - tailored suits, turtlenecks, bold. Rectangle silhouette.
- The 'Mod' look.
- 1970s - Hippy to Disco Era. Unisex,
- Men and Women both wore bold flower prints, platform shoes, bell bottoms, wide ties and collars. triangle silhouette.
- 1980s - Yuppie Era.
- Women - exercise wear as everyday clothes, bold bright colors, inverted triangle silhouette.
- Men - business suits with narrow detailing, suspenders, pastels. rectangle silhouette.
- Logo wear, designer jeans.
- 1990s - The Dot Com Era. Rejection of fashion, grunge.
- Women - Bare midriff, rectangle silhouette.
- Men - baggy pants, big sneakers, rectangle silhouette.
- 2000s - Wired generation.
- Both men and women wore Skinny jeans, embellishments, hip-hop style.
- 2010s - Social media Rise of androgyny.
- Both men and women wear Leggings, jeggings, cutouts, hipster-style. (Look at what you're wearing today, what will people remember?)
- 1890's - Victorian Era.
Standard 4
Identify and discuss characteristics of fashion global capitals and designers.
-
Major Fashion Capitals:
- Paris, France - (First Fashion capital) French fashion is chic and stylish. Defined by its sophistication, tailored cut, and smart accessories. Most designers based in other capitals have a boutique in Paris.
- New York City, New York, USA - (Merchandising capital) American fashion is sophisticated, clean cut and casual. Use of separates, sportswear and natural fibers.
- Milan, Italy - (Elegance and luxurious fabrics) Italian fashion features casual elegance and luxurious fabrics such as Merino wool and leather.
- London, England - (Modern British designers tend to favor a "rebel" street look) London is known for conservative cuts and traditional styles of the upper class (stores based in the Mayfield area, specifically Savile Row). The young embrace an individualistic style, and this is the real impact in modern fashion. The UK is the home of the punk movement.
- Tokyo, Japan - (Asian influence, loose and unstructured) Typically considered somber subtle and richly textured, pattern added through complicated cutting and sewing and applique. The young Japanese are favoring the Harajuku look inspired by anime.
-
Designers of influence
- Charles Worth - the father of couture.
- Coco Chanel - the little black dress, costume jewelry, unstructured.
- Christian Dior - "the new look" hourglass silhouette with exaggerated lower half.
- Ralph Lauren - designer for the "American West." Sophisticated and sellable.
- There are many designers of influence throughout history. They are covered in more detail in Design Merchandising. (Pathway - Fashion, Apparel and Textiles)
Standard 5
Identify fashion related careers
-
costume designer - a person who designs costumes for film, stage production or television.
-
museum curator - one who manages or oversees as the administrative director of a museum, collection or library. Care for historical clothing includes light, temperature and humidity control.
Performance Skills
Complete FCCLA Step One and/or introduce DECA. http://www.uen.org/cte/facs_cabinet/facs_cabinet10.shtml
http://www.deca.org
Strand 2
Students will recognize and apply the principles and elements of fashion design and associated careers.
Standard 1
Demonstrate knowledge of the elements (tools) of design.
-
Line
- Vertical - Straight up and down, formal. Adds height and a creates a narrow, taller silhouette.
- Horizontal - Straight side to side, informal. Adds width, solidity and reduces height.
- Diagonal - Straight at an angle, creates excitement and energy. Reflects the same illusion as the straight line they most resemble.
- Curved - Not straight, creates a softening effect. Adds movement, can reemphasize and define.
-
Shape/clothing silhouette
-
Color
- Color basics:
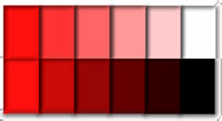
 Hue - another term for color
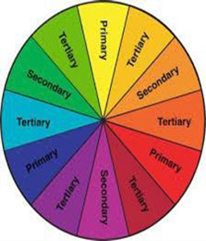
Hue - another term for color - Primary - pure hues that cannot be made from other colors. Red, yellow, blue.
- Secondary - created by combining two primary colors. Orange, green, violet.
- Tertiary/intermediate - created by combining a primary and secondary color. Red-orange, red-violet, yellow-orange, yellow-green, blue-green, blue-violet.
- Cool - yellow-green through violet.
- Warm - red-violet through yellow.
- Color basics:
-
Value lightness or darkness of a hue
-
Intensity: brightness or dullness of a hue
- Tones - hue + gray or complement

- Schemes:
- Neutral - black, white, tan, brown

- Accented neutral - mostly neutral with just a touch of color
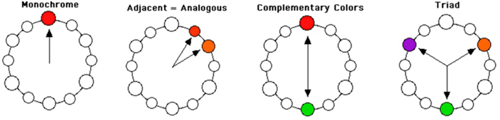
- Monochromatic - tints, shades and tones of one color
- Triadic - three colors evenly spaces on the wheel
- Analogous - 2-4 colors next to each other on the wheel
- Complementary - two colors opposite on the color wheel
- Texture
- Pattern
Standard 2
Demonstrate knowledge of the principles (rules) of design.-
Proportion/Scale -the relationship between the size of parts or objects in a design.
-
Balance:
-
Emphasis: focal point
-
Rhythm:
- Gradation - gradual change in size orcolor.
- Opposition - direct contrast created by perpendicular lines, black and white or complementary colors placed next to each other.
- Radiation - lines extending from a central point.
- Repetition - line, color or pattern repeated.
- Transition - curved lines that lead from one area of a design to another.
-
Harmony: a relationship in which unity and variety exist together.
Standard 3
Identify related careers.-
Fashion Designer - The art of applying design, aesthetics and natural beauty to clothing and its accessories.
-
Illustrator - a person who creates images of clothes for magazines, books, advertising, social media, etc.
Performance Skills
Create a color wheel identifying primary, secondary, and tertiary/intermediate colors, the warm and cool colors, and tints and shades.Performance Skills
Create a fashion project or professional presentation incorporating the principles and elements of design; explain in writing, (design, portfolio, power point, display, etc.).
Strand 3
Students will examine the use of textiles in fashion and associated careers.Standard 1
Identify the basic fibers and characteristics of manufactured and natural textiles. Recognize that fiber content establishes many of the characteristics of a specific fabric.-
Identify natural fibers (e.g., cotton, linen, silk, wool) and their characteristics.
- General characteristics: come from plants and animals, moisture absorbent.
- Cotton: plant source
- Pros -absorbent, comfortable, durable, easy to launder, stronger wet than dry.
- Cons -wrinkles, shrinks mildew.
- Linen: plant source. (flax)
- Pros -absorbent, natural luster, quick drying.
- Cons -wrinkles, frays, little stretch, mildew.
- Silk: animal source. (silkworm cocoon)
- Pros -absorbent, natural luster, insulating, strong, resilient.
- Cons -degrades and yellows from age and sunlight weaker wet than dry, water marks.
- Wool: animal source (fur).
- Pros -absorbent, strong, elastic, flame resistant, wrinkle resistant.
- Cons -shrinks when laundered improperly, bleaches with sunlight, damaged by moths.
- Cotton: plant source
- General characteristics: come from plants and animals, moisture absorbent.
-
Identify manufactured fibers (e.g., nylon, polyester, bamboo, rayon, spandex, and their characteristics).
-
General characteristics: made from chemical processes (some made from natural elements mixed with chemicals while others are made completely from non-natural substances)
- Nylon: Chemical source.
- Pros -strong, water repellent, colorfast, abrasion resistant.
- Cons -frays easily, heat sensitive, non-recyclable.
- Polyester: Chemical source.
- Pros-good shape retention, easy to launder, wrinkle resistant, colorfast, blends well with other fibers.
- Cons -retains oily stains, pills, builds static.
- Rayon: Cellulose source.
- Pros-soft and comfortable, drapes well, blends well with other fibers, dyes well.
- Cons-shrinks, poor shape retention, wrinkles. Dry clean only.
- Spandex: Chemical source.
- Pros -very elastic, adds stretch when blended with other fibers, resistant to oils and outdoor elements. (sun, sea and sand)
- Cons -shrinks, damaged by heat, can be difficult to sew.
- Bamboo: Cellulose source.
- Pros -soft, strong, water absorbent, renewable.
- Cons -wrinkles, takes longer to dry and yellow with time.
- Nylon: Chemical source.
-
Identify advantages of blended fibers used in fabrics (i.e. they combine thebest characteristics of two or more fibers).
Standard 2
Examine the construction of fabric.-
Identify the characteristics of woven, knit (looping yarns), and non-woven fabrics.
-
Classify dye processes.
Standard 3
Identify textile production related careers.-
Textile Designer - create design for woven, knitted or printed fabrics.
-
Textile Chemist - research and development of fibers, yarns and dyeing through sustainable processes.
Performance Skills
Create a fabric reference guide consisting of natural/manufactured fibers and woven/knit fabrics.
Strand 4
Students will identify consumer strategies in the fashion industry and associated careers.Standard 1
Identify consumer influences.-
Cultural and social - ethnicity, religion, values, conformity, peer pressure, and individuality.
-
Economic conditions - affordability, availability, lifestyle, and political climate.
-
Media and advertising - commercials, movies, TV, magazines, social media, and celebrities.
-
Technology - new developments, research, and environmental impact.
Standard 2
Identify various types of retail options.-
Chain Store - a group of stores owned, managed, and controlled by a central office. Examples: Gap, Forever 21, American Eagle.
-
Department Store - retail stores that offer large varieties of many types of merchandise place in appropriate departments. Examples: Macy's, Dillard's, JCPenney.
-
Specialty Store - stores that sell a specific type or limited line of goods. Examples: Victoria's Secret, Claire's, Foot Locker.
-
Discount Store - stores that sell mass market merchandise in large, simple buildings with low overhead. Examples: Target, Kohl's, Wal-Mart.
-
Manufacturer-owned Store - stores that carry merchandise made specifically for that label or brand. Examples: Nike, Ralph Lauren, Lululemon.
-
Outlet Store - Manufacturer-owned discount stores which sell seconds and over-runs.
-
E-commerce - online purchasing alternative options for brick and mortar.
Standard 3
Identify consumer skills.-
Judging quality (basic construction, seams, matching plaid, attachment of fasteners)
-
Cost per wear (price of garment/number of times worn).
-
Smart shopping (sales, comparison shop, coupons, membership clubs, calculating discounts).
-
Labels (required by law: fiber content, garment care, international care symbols, manufacturer number, country oforigin).
-
Hang tags (optional: brand name, advertising, logo, etc.)
Standard 4
Identify related careers.-
Buyer - purchase lines of clothing, shoes and fashion accessories to be sold at retail stores.
-
Retail sales - assist the customer in a brick and mortar store to facilitate their purchase.
-
Manufacturing sales representative - sell wholesale or manufactured goods to buyers.
-
Marketing - oversee branding and advertising of a company's products.
Performance Skills
Students will demonstrate consumer math by calculating cost per wear and percentage discounts off retail price. Student will judge value of a clothing item by comparing quality to cost.
Strand 5
Students will evaluate personal fashion characteristics and associated careers.Standard 1
Aspects of personal appearance.Standard 2
Identify and analyze wardrobe needs for a personal lifestyle.-
Basic pieces - Classic, well-constructed, cost per wear, neutral + a favorite color. (i.e. Long sleeve T-shirt, Short sleeve T-shirt, Tank top, Collared shirt, Light weight cardigan, Little black dress, Jeans, and Dress pants)
-
Trendy - items that are currently in style based on design details and elements of design.
Standard 3
Identify related careers.-
Fashion Stylist - Selects clothes and accessories for magazine spreads and celebrities.
-
Fashion Consultant - Advises individuals on their personal fashion choices, includes personal shopping, closet audits, beauty and style consultations.
Performance Skills
Create a visual representation of a personal wardrobe using eight basic and six trendy pieces. Accessorize based on personal taste. Write a description that explains how this collection expresses your personal fashion characteristics.Workplace Skills
Students will develop professional and interpersonal skills needed for success in the fashion industry.-
Determine the difference between hard skills and soft skills.
-
Identify soft skills needed in the workplace
 http://www.uen.org - in partnership with Utah State Board of Education
(USBE) and Utah System of Higher Education
(USHE). Send questions or comments to USBE
Specialist -
Kristina
Yamada
and see the CTE/Arts, Audio/Visual Technology and Communication website. For
general questions about Utah's Core Standards contact the Director
-
THALEA
LONGHURST.
These materials have been produced by and for the teachers of the
State of Utah. Copies of these materials may be freely reproduced
for teacher and classroom use. When distributing these materials,
credit should be given to Utah State Board of Education. These
materials may not be published, in whole or part, or in any other
format, without the written permission of the Utah State Board of
Education, 250 East 500 South, PO Box 144200, Salt Lake City, Utah
84114-4200.
http://www.uen.org - in partnership with Utah State Board of Education
(USBE) and Utah System of Higher Education
(USHE). Send questions or comments to USBE
Specialist -
Kristina
Yamada
and see the CTE/Arts, Audio/Visual Technology and Communication website. For
general questions about Utah's Core Standards contact the Director
-
THALEA
LONGHURST.
These materials have been produced by and for the teachers of the
State of Utah. Copies of these materials may be freely reproduced
for teacher and classroom use. When distributing these materials,
credit should be given to Utah State Board of Education. These
materials may not be published, in whole or part, or in any other
format, without the written permission of the Utah State Board of
Education, 250 East 500 South, PO Box 144200, Salt Lake City, Utah
84114-4200.
- Schemes:
- Tones - hue + gray or complement


 UTAH EDUCATION NETWORK
UTAH EDUCATION NETWORK

 Justin
Justin Braxton
Braxton Dani
Dani Kayla
Kayla Katie
Katie Lora
Lora Rob
Rob Val
Val