 SEEd - Grade 1
SEEd - Grade 1
 Printable Version (pdf)
Printable Version (pdf)
 Course Introduction
Course Introduction
Utah Science with Engineering Education Standards
Utah’s Science and Engineering Education (SEEd) standards were written by Utah educators and scientists, using a wide array of resources and expertise. A great deal is known about good science instruction. The writing team used sources including A Framework for K–12 Science Education1, the Next Generation Science Standards2, and related works to craft research-based standards for Utah. These standards were written with students in mind, including developmentally appropriate progressions that foster learning that is simultaneously age-appropriate and enduring. The aim was to address what an educated citizenry should know and understand to embrace the value of scientific thinking and make informed decisions. The SEEd standards are founded on what science is, how science is learned, and the multiple dimensions of scientific work.
Principles of Scientific Literacy
Science is a way of knowing, a process for understanding the natural world. Engineering applies the fields of science, technology, and mathematics to produce solutions to real-world problems. The process of developing scientific knowledge includes ongoing questioning, testing, and refinement of ideas when supported by empirical evidence. Since progress in modern society is tied so closely to this way of knowing, scientific literacy is essential for a society to be engaged in political and economic choices on personal, local, regional, and global scales. As such, the Utah SEEd standards are based on the following essential elements of scientific literacy.
Science is valuable, relevant, and applicable.
Science produces knowledge that is inherently important to our society and culture. Science and engineering support innovation and enhance the lives of individuals and society. Science is supported from and benefited by an equitable and democratic culture. Science is for all people, at all levels of education, and from all backgrounds.
Science is a shared way of knowing and doing.
Science learning experiences should celebrate curiosity, wonder, skepticism, precision, and accuracy. Scientific habits of mind include questioning, communicating, reasoning, analyzing, collaborating, and thinking critically. These values are shared within and across scientific disciplines, and should be embraced by students, teachers, and society at large.
Science is principled and enduring.
Scientific knowledge is constructed from empirical evidence; therefore, it is both changeable and durable. Science is based on observations and inferences, an understanding of scientific laws and theories, use of scientific methods, creativity, and collaboration. The Utah SEEd standards are based on current scientific theories, which are powerful and broad explanations of a wide range of phenomena; they are not simply guesses nor are they unchangeable facts. Science is principled in that it is limited to observable evidence. Science is also enduring in that theories are only accepted when they are robustly supported by multiple lines of peer reviewed evidence. The history of science demonstrates how scientific knowledge can change and progress, and it is rooted in the cultures from which it emerged. Scientists, engineers, and society, are responsible for developing scientific understandings with integrity, supporting claims with existing and new evidence, interpreting competing explanations of phenomena, changing models purposefully, and finding applications that are ethical.
Principles of Science Learning
Just as science is an active endeavor, students best learn science by engaging in it. This includes gathering information through observations, reasoning, and communicating with others. It is not enough for students to read about or watch science from a distance; learners must become active participants in forming their ideas and engaging in scientific practice. The Utah SEEd standards are based on several core philosophical and research-based underpinnings of science learning.
Science learning is personal and engaging.
Research in science education supports the assertion that students at all levels learn most when they are able to construct and reflect upon their ideas, both by themselves and in collaboration with others. Learning is not merely an act of retaining information but creating ideas informed by evidence and linked to previous ideas and experiences. Therefore, the most productive learning settings engage students in authentic experiences with natural phenomena or problems to be solved. Learners develop tools for understanding as they look for patterns, develop explanations, and communicate with others. Science education is most effective when learners invests in their own sense-making and their learning context provides an opportunity to engage with real-world problems.
Science learning is multi-purposed.
Science learning serves many purposes. We learn science because it brings us joy and appreciation but also because it solves problems, expands understanding, and informs society. It allows us to make predictions, improve our world, and mitigate challenges. An understanding of science and how it works is necessary in order to participate in a democratic society. So, not only is science a tool to be used by the future engineer or lab scientist but also by every citizen, every artist, and every other human who shares an appreciation for the world in which we live.
All students are capable of science learning.
Science learning is a right of all individuals and must be accessible to all students in equitable ways. Independent of grade level, geography, gender, economic status, cultural background, or any other demographic descriptor, all K–12 students are capable of science learning and science literacy. Science learning is most equitable when students have agency and can engage in practices of science and sense-making for themselves, under the guidance and mentoring of an effective teacher and within an environment that puts student experience at the center of instruction. Moreover, all students are capable learners of science, and all grades and classes should provide authentic, developmentally appropriate science instruction.
Three Dimensions of Science
Science is composed of multiple types of knowledge and tools. These include the processes of doing science, the structures that help us organize and connect our understandings, and the deep explanatory pieces of knowledge that provide predictive power. These facets of science are represented as “three dimensions” of science learning, and together these help us to make sense of all that science does and represents. These include science and engineering practices, crosscutting concepts, and disciplinary core ideas. Taken together, these represent how we use science to make sense of phenomena, and they are most meaningful when learned in concert with one another. These are described in A Framework for K–12 Science Education, referenced above, and briefly described here:
Science and Engineering Practices (SEPs):
Practices refer to the things that scientists and engineers do and how they actively engage in their work. Scientists do much more than make hypotheses and test them with experiments. They engage in wonder, design, modeling, construction, communication, and collaboration. The practices describe the variety of activities that are necessary to do science, and they also imply how scientific thinking is related to thinking in other subjects, including math, writing, and the arts. For a further understanding of science and engineering practices see Chapter 3 in A Framework for K–12 Science Education.
Crosscutting Concepts (CCCs):
Crosscutting concepts are the organizing structures that provide a framework for assembling pieces of scientific knowledge. They reach across disciplines and demonstrate how specific ideas are united into overarching principles. For example, a mechanical engineer might design some process that transfers energy from a fuel source into a moving part, while a biologist might study how predators and prey are interrelated. Both of these would need to model systems of energy to understand how all of the features interact, even though they are studying different subjects. Understanding crosscutting concepts enables us to make connections among different subjects and to utilize science in diverse settings. Additional information on crosscutting concepts can be found in Chapter 4 of A Framework for K-12 Science Education.
Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCIs):
Core ideas within the SEEd Standards include those most fundamental and explanatory pieces of knowledge in a discipline. They are often what we traditionally associate with science knowledge and specific subject areas within science. These core ideas are organized within physical, life, and earth sciences, but within each area further specific organization is appropriate. All these core ideas are described in chapters 5 through 8 in the K–12 Framework text, and these are employed by the Utah SEEd standards to help clarify the focus of each strand in a grade level or content area.
Even though the science content covered by SEPs, CCCs, and DCIs is substantial, the Utah SEEd standards are not meant to address every scientific concept. Instead, these standards were written to address and engage in an appropriate depth of knowledge, including perspectives into how that knowledge is obtained and where it fits in broader contexts, for students to continue to use and expand their understandings over a lifetime.
Articulation of SEPs, CCCs, and DCIs
| Science and Engineering Practices |
Crosscutting Concepts |
Disciplinary Core Ideas |
Asking questions or defining problems:
Students engage in asking testable questions and defining problems to pursue understandings of phenomena.
Developing and using models:
Students develop physical, conceptual, and other models to represent relationships, explain mechanisms, and predict outcomes.
Planning and carrying out investigations:
Students plan and conduct scientific investigations in order to test, revise, or develop explanations.
Analyzing and interpreting data:
Students analyze various types of data in order to create valid interpretations or to assess claims/conclusions.
Using mathematics and computational thinking:
Students use fundamental tools in science to compute relationships and interpret results.
Constructing explanations and designing solutions:
Students construct explanations about the world and design solutions to problems using observations that are consistent with current evidence and scientific principles.
Engaging in argument from evidence:
Students support their best explanations with lines of reasoning using evidence to defend their claims.
Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information:
Students obtain, evaluate, and derive meaning from scientific information or presented evidence using appropriate scientific language. They communicate their findings clearly and persuasively in a variety of ways including written text, graphs, diagrams, charts, tables, or orally. |
Patterns:
Students observe patterns to organize and classify factors that influence relationships
Cause and effect:
Students investigate and explain causal relationships in order to make tests and predictions.
Scale, proportion, and quantity:
Students compare the scale, proportions, and quantities of measurements within and between various systems.
Systems and system models:
Students use models to explain the parameters and relationships that describe complex systems.
Energy and matter:
Students describe cycling of matter and flow of energy through systems, including transfer, transformation, and conservation of energy and matter.
Structure and function:
Students relate the shape and structure of an object or living thing to its properties and functions.
Stability and change:
Students evaluate how and why a natural or constructed system can change or remain stable over time. |
Physical Sciences:
(PS1) Matter and Its Interactions
(PS2) Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions
(PS3) Energy
(PS4) Waves
Life Sciences:
(LS1) Molecules to Organisms
(LS2) Ecosystems
(LS3) Heredity
(LS4) Biological Evolution
Earth and Space Sciences:
(ESS1) Earth’s Place in the Universe
(ESS2) Earth’s Systems
(ESS3) Earth and Human Activity
Engineering Design:
(ETS1.A) Defining and Delimiting an Engineering Problem
(ETS1.B) Developing Possible Solutions
(ETS1.C) Optimizing the Design Solution |
Organization of Standards
The Utah SEEd standards are organized into strands which represent significant areas of learning within grade level progressions and content areas. Each strand introduction is an orientation for the teacher in order to provide an overall view of the concepts needed for foundational understanding. These include descriptions of how the standards tie together thematically and which DCIs are used to unite that theme. Within each strand are standards. A standard is an articulation of how a learner may demonstrate their proficiency, incorporating not only the disciplinary core idea but also a crosscutting concept and a science and engineering practice. While a standard represents an essential element of what is expected, it does not dictate curriculum—it only represents a proficiency level for that grade. While some standards within a strand may be more comprehensive than others, all standards are essential for a comprehensive understanding of a strand’s purpose.
The standards of any given grade or course are not independent. SEEd standards are written with developmental levels and learning progressions in mind so that many topics are built upon from one grade to another. In addition, SEPs and CCCs are especially well paralleled with other disciplines, including English language arts, fine arts, mathematics, and social sciences. Therefore, SEEd standards should be considered to exist not as an island unto themselves, but as a part of an integrated, comprehensive, and holistic educational experience.
Each standard is framed upon the three dimensions of science to represent a cohesive, multi-faceted science learning outcome.
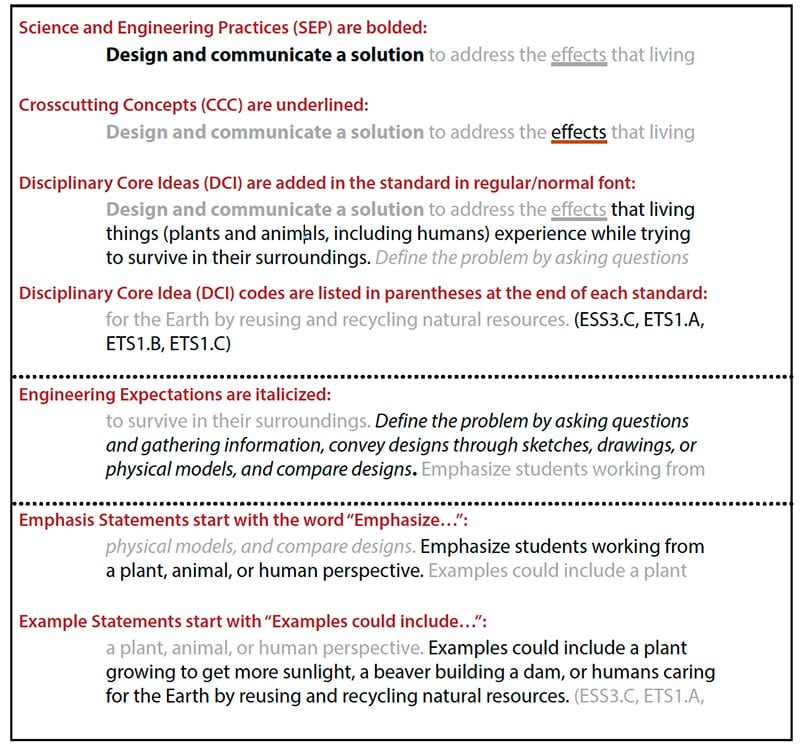
- Within each SEEd Standard Science and Engineering Practices are bolded.
- Crosscutting Concepts are underlined.
- Disciplinary Core Ideas are added to the standard in normal font with the relevant DCIs codes from the K–12 Framework (indicated in parentheses after each standard) to provide further clarity.
- Standards with specific engineering expectations are italicized.
- Many standards contain additional emphasis and example statements that clarify the learning goals for students.
- Emphasis statements highlight a required and necessary part of the student learning to satisfy that standard.
- Example statements help to clarify the meaning of the standard and are not required for instruction.
An example of a SEEd standard:
- Standard K.2.4 Design and communicate a solution to address the effects that living things (plants and animals, including humans) experience while trying to survive in their surroundings. Define the problem by asking questions and gathering information, convey designs through sketches, drawings, or physical models, and compare designs. Emphasize students working from a plant, animal, or human perspective. Examples could include a plant growing to get more sunlight, a beaver building a dam, or humans caring for the Earth by reusing and recycling natural resources. (ESS3.C, ETS1.A, ETS1.B, ETS1.C)
Each part of the above SEEd standard is identified in the following diagram:
Goal of the SEEd Standards
The Utah SEEd Standards is a research-grounded document aimed at providing accurate and appropriate guidance for educators and stakeholders. But above all else, the goal of this document is to provide students with the education they deserve, honoring their abilities, their potential, and their right to utilize scientific thought and skills for themselves and the world that they will build.
1 National Research Council. 2012. A Framework for K–12 Science Education: Practices, Crosscutting Concepts, and Core Ideas. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/13165. This consensus research document and its chapters are referred to throughout this document as a research basis for much of Utah’s SEEd standards.
2 Most Utah SEEd Standards are based on the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS Lead States. 2013. Next Generation Science Standards: For States, By States. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press) http://www. nextgenscience.org
Introduction
The first-grade SEEd standards provide a framework for students to obtain, evaluate,
and communicate information about seasonal and space patterns. Students investigate
the needs of all living things including their offspring. Students model and investigate
the effects of light and sound on objects or the effects of objects on light and sound.
Additionally, students design and evaluate solutions to problems that exist in these areas.
Core Standards of the Course
Strand 1.1: SEASONS AND SPACE PATTERNS
Seasonal patterns of motion of the Sun, Moon, and stars can be observed, described, and predicted. These patterns may vary depending on the region, location, or time of year.
Standard 1.1.1
Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the movement of the Sun, Moon, and stars to describe predictable patterns. Examples of patterns could include how the Sun and Moon appear to rise in one part of the sky, move across the sky, and set; or how stars, other than the Sun, are visible at night but not during the day. (ESS1.A)

Standard 1.1.2
Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the patterns observed at different times of the year to relate the amount of daylight to the time of year. Emphasize the variation in daylight patterns at different times of the day and different times of the year. Examples could include varying locations and regions throughout the state, country, and world. (ESS1.B)

Standard 1.1.3
Design a device that measures the varying patterns of daylight. Define the problem by asking questions and gathering information, convey designs through sketches, drawings, or physical models, and compare and test designs. Examples could include sundials for telling the time or tracking the movement of shadows throughout the day. (ESS1.B, ETS1.A, ETS1.B, ETS1.C)

Strand 1.2: THE NEEDS OF LIVING THINGS AND THEIR OFFSPRING
Living things (plants and animals, including humans) depend on their surroundings to get what they need, including food, water, shelter, and a favorable temperature. Plants and animals have external features that allow them to survive in a variety of environments. Young plants and animals are similar but not exactly like their parents. In many kinds of animals, parents and offspring engage in behaviors that help the offspring to survive.
Standard 1.2.1
Plan and carry out an investigation to determine the effect of sunlight and water on plant growth. Emphasize investigations that test one variable at a time. (LS1.C)

Standard 1.2.2
Construct an explanation by observing patterns of external features of living things that survive in different locations. Emphasize how plants and nonhuman animals, found in specific surroundings, share similar physical characteristics. Examples could include that plants living in dry areas are more likely to have thick outer coatings that hold in water, animals living in cold locations have longer and thicker fur, or most desert animals are awake at night. (LS1.A, LS1.D)

Standard 1.2.3
Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the patterns of plants and nonhuman animals that are alike, but not exactly like, their parents. An example could include that most carrots are orange and shaped like a cone but may be different sizes or have differing tastes. (LS3.A, LS3.B)

Standard 1.2.4
Construct an explanation of the patterns in the behaviors of parents and offspring which help offspring to survive. Examples of behavioral patterns could include the signals that offspring make such as crying, chirping, and other vocalizations or the responses of the parents such as feeding, comforting, and protecting the offspring. (LS1.B)

Strand 1.3: LIGHT AND SOUND
Sound can make matter vibrate, and vibrating matter can make sound. Objects can only be seen when light is available to illuminate them. Some objects give off their own light. Some materials allow light to pass through them, others allow only some light to pass through them, and still others block light and create a dark shadow on the surface beyond them where the light cannot reach. Mirrors can be used to redirect light. People use a variety of devices that may include sound and light to communicate over long distances.
Standard 1.3.1
Plan and carry out an investigation to show the cause and effect relationship between sound and vibrating matter. Emphasize that vibrating matter can make sound and that sound can make matter vibrate. (PS4.A)

Standard 1.3.2
Use a model to show the effect of light on objects. Emphasize that objects can be seen when light is available to illuminate them or if they give off their own light. (PS4.B)

Standard 1.3.3
Plan and carry out an investigation to determine the effect of materials in the path of a beam of light. Emphasize that light can travel through some materials, can be reflected off some materials, and some materials block light causing shadows. Examples of materials could include clear plastic, wax paper, cardboard, or a mirror. (PS4.B)

Standard 1.3.4
Design a device in which the structure of the device uses light or sound to solve the problem of communicating over a distance. Define the problem by asking questions and gathering information, convey designs through sketches, drawings, or physical models, and compare and test designs. Examples of devices could include a light source to send signals, paper-cup-and-string telephones, or a pattern of drum beats. (PS4.C, ETS1.A, ETS1.B, ETS1.C)

 http://www.uen.org - in partnership with Utah State Board of Education
(USBE) and Utah System of Higher Education
(USHE). Send questions or comments to USBE
Specialist -
Jennifer
Throndsen
and see the Science - Elementary website. For
general questions about Utah's Core Standards contact the Director
-
Jennifer
Throndsen.
These materials have been produced by and for the teachers of the
State of Utah. Copies of these materials may be freely reproduced
for teacher and classroom use. When distributing these materials,
credit should be given to Utah State Board of Education. These
materials may not be published, in whole or part, or in any other
format, without the written permission of the Utah State Board of
Education, 250 East 500 South, PO Box 144200, Salt Lake City, Utah
84114-4200.
http://www.uen.org - in partnership with Utah State Board of Education
(USBE) and Utah System of Higher Education
(USHE). Send questions or comments to USBE
Specialist -
Jennifer
Throndsen
and see the Science - Elementary website. For
general questions about Utah's Core Standards contact the Director
-
Jennifer
Throndsen.
These materials have been produced by and for the teachers of the
State of Utah. Copies of these materials may be freely reproduced
for teacher and classroom use. When distributing these materials,
credit should be given to Utah State Board of Education. These
materials may not be published, in whole or part, or in any other
format, without the written permission of the Utah State Board of
Education, 250 East 500 South, PO Box 144200, Salt Lake City, Utah
84114-4200.
 Course Introduction
Course Introduction













 UTAH EDUCATION NETWORK
UTAH EDUCATION NETWORK

 Justin
Justin Braxton
Braxton Dani
Dani Kayla
Kayla Katie
Katie Lora
Lora Rob
Rob Val
Val

