 Course Introduction
Course Introduction
Core Standards of the Course
Strand 1
Students will identify the role and characteristics of an entrepreneur. Students will examine the benefits and risks of entrepreneurship activity to the economy.
Standard 1
Students will explore to the role of the entrepreneur within the economy.
-
Define and differentiate between an entrepreneur, entrepreneurship, and intrapreneur.
-
Understand the characteristics, ethics, and risk of entrepreneurship.
-
Explore the importance of failure within the entrepreneurial venture.
-
Discuss why entrepreneurship is beneficial to the economy (local, national, global).
-
Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of buying an existing business, starting a new business, starting a partnership, purchasing a franchise.
-
Identify organizations that support entrepreneurs (SBDC, SBA, SCORE, GOED).
-
Understand government's role and effect in entrepreneurship (regulations, taxes, subsidies, as a consumer).
Performance Skills
Advantages and disadvantages of being an entrepreneur in a specific industry and/or explore the successes and failures of influential entrepreneurs.
Workplace Skills
Students will connect their knowledge with current workplace skills including:
Strand 2
Students will identify problems and create solutions in order to address consumers' needs/wants.
Standard 1
Students will understand idea generation through innovation and problem solving.
-
Understand the purpose of the Lean Canvas model (see image below).
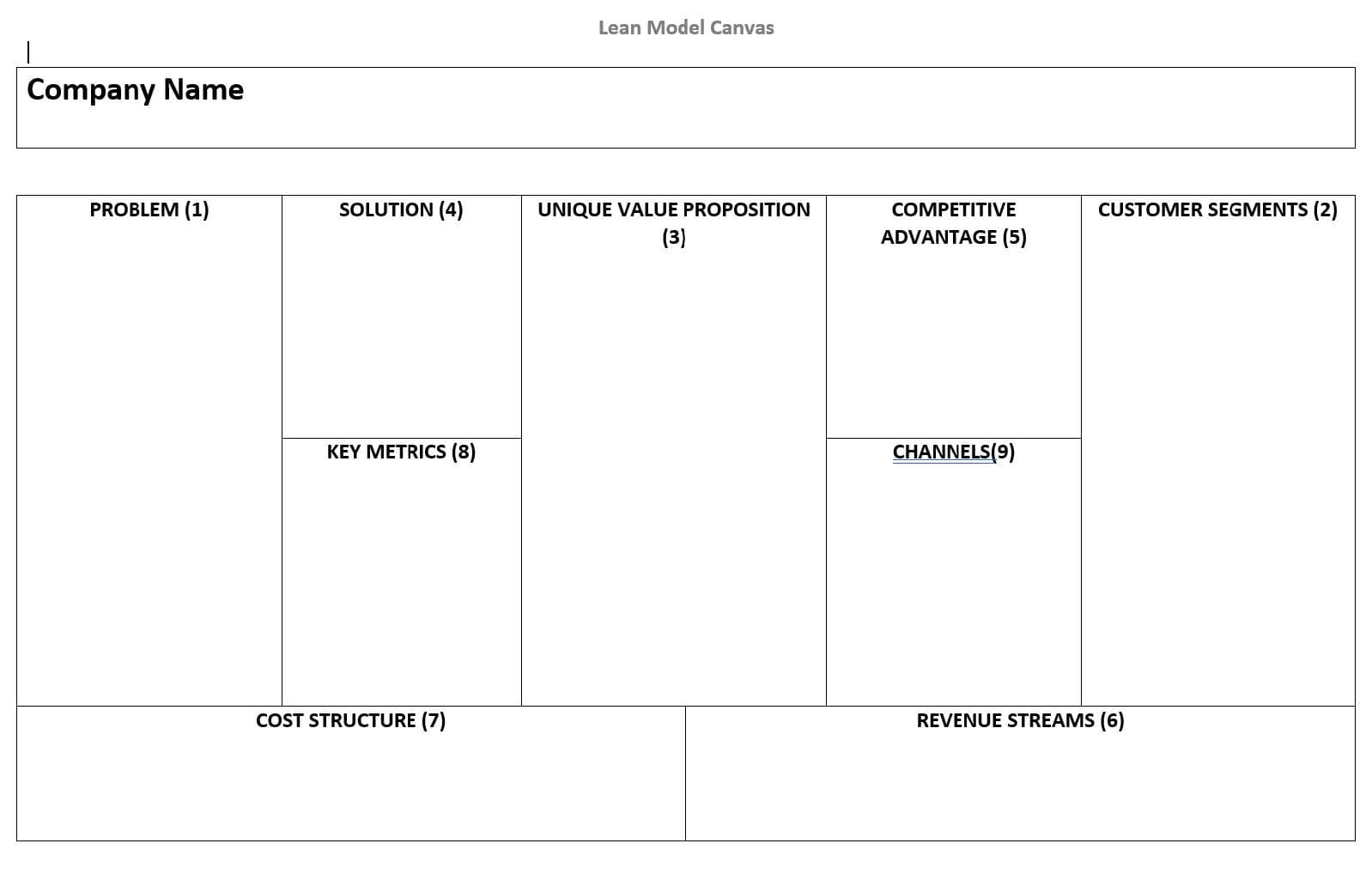
-
Identify problems to address needs and/or wants by using various methods of ideageneration (e.g. identifying trends, brainstorming, brain writing, market research).
-
Explore trends in entrepreneurship (emerging technologies, social entrepreneurship, green entrepreneurship, crowdsourcing/funding, technopreneurship).
-
Define and give examples of market segmentation methods (demographics, psychographics, behavioral, geographical).
-
Identify target markets for potential new businesses.
-
Understand the importance of pivoting to solve entrepreneurial problems.
Standard 2
Students will understand how to solve your customers' needs and wants and identify what distinguishes a product/service from the competition (minimum viable product (MVP), unique value proposition (UVP), competitive advantage).
Performance Skills
Students will complete steps 1 - 5 of the Lean Canvas model.
-
Step 1-Problem
-
Step 2-Customer Segments
-
Step 3-Unique Value Proposition
-
Step 4-Solution
-
Step 5-Competitive Advantage
Workplace Skills
Students will connect their knowledge with current workplace skills including:
Strand 3
Students will understand how economic concepts effect decision making in an entrepreneurial venture.
Standard 1
Students will understand basic economic terminology.
-
Explain the determinants of supply and demand.
-
Understand opportunity cost and scarcity.
-
Describe the interrelationship between cost and price.
-
Describe the concepts of import and export.
Strand 4
Students will understand how marketing affects an entrepreneurial venture.
Standard 1
Students will understand the marketing functions.
-
Identify the elements of the marketing mix (Product, Price, Place, Promotion).
-
Analyze the advantages and disadvantages of possible locations for businesses(brick-and-mortar stores, online, click-and-mortar, service).
-
Understand the distribution channels available to effectively reach a target market.
Standard 2
Students will evaluate the promotional mix.
-
Discuss the impact of competition on keeping/increasing market share and be ableto complete a competitor analysis.
-
Identify the elements of the promotional mix (advertising, public relations, salespromotions, personal selling).
-
Discuss effective digital marketing activities for a company.
-
Discuss the importance of a company's online presence (i.e. social media posts/platforms, customer reviews, and testimonials).
-
Understand digital analytics and customer metrics used in marketing (customer acquisition costs, repeat/new customers, lifetime value, and profitability).
Performance Skills
Students will create a promotion using at least one of the elements of the promotional mix. And complete steps 8 - 9 of Lean Canvas model.
Workplace Skills
Students will connect their knowledge with current workplace skills including:
Strand 5
Students will understand financial concepts and tools used by entrepreneurs in making business decisions.
Standard 1
Students will examine financial concepts and types of funding used to operate a business.
-
Project expenses (start-up costs, variable costs, fixed costs, operational expenses), income, net profit, gross profit, and break-even point.
-
Describe common sources by which entrepreneurs can secure funding (angel investors, venture capitalists, crowd funding, credit lines, personal savings, family and friends, mortgage, small business loan, grants, bootstrapping, IPO).
-
Describe entrepreneurship mentoring trends and entrepreneurship contests (e.g., boom start-up, incubators, business plan/pitch contests).
-
Compare and contrast debt and equity financing. Identify the advantages and disadvantages of different types of financing options for entrepreneurs.
-
Understand the importance of pitching in the fundraising process.
Standard 2
Students will understand how entrepreneurs utilize business records.
-
Discuss the impact of incomplete and/or inaccurate business records on a business (e.g., sales receipts, expense records, taxes, etc.).
-
Explore various systems for handling sales (POS: point-of-sales), inventory, and payments (ex: PayPal, Square, Venmo, Apple Pay).
-
Describe basic types of accounting systems (accrual, cash, tax).
-
Identify and explain common financial statements (income statements/profit andloss statements, balance sheets).
-
Understand the importance of sales and budget forecasting in business planning.
Performance Skills
Students will complete steps 6-7 in Lean Canvas model. If needed, revisit step 8
-
Step 6-Revenue Streams
-
Step 7-Cost Structures
AND (Complete at least one of the following)
-
Calculate break-even point.
-
Create a financial statement.
-
Compare and contrast various payment systems.
-
Use a spreadsheet tool (What-If analysis) for modeling, projections, and forecasting.
Workplace Skills
Students will connect their knowledge with current workplace skills including:
Strand 6
Students will understand the role of management principles in an entrepreneurial venture.
Standard 1
Students will discuss the importance of goal setting for an entrepreneurial venture (mission and vision statements).
Standard 2
Students will understand different types of organizational structures and the importance of job descriptions for a business.
Performance Skills
Students will complete one of the following:
-
Create a mission statement and vision statement.
-
Create an organizational structure.
-
Develop job descriptions for positions.
Strand 7
Students will analyze how forms of business ownership, government regulations, and legal regulations affect entrepreneurial ventures.
Standard 1
Students will compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of the different types of business ownership (sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, LLC, nonprofit). Students will understand the importance of a business plan when forming a business.
Standard 2
Students will understand government and legal regulations that affect entrepreneurial ventures.
-
Identify licenses that a small business must obtain (e.g., business license, EIN, name registry, sales tax I.D., occupational/professional license, food handlers).
-
Identify taxes businesses pay (income, sales, property, payroll).
-
Identify ways of protecting ideas and inventions (copyright, patent, trademark).
-
Identify types of business insurance and employee benefits (e.g. worker's compensation, liability, 401K, health, Medicare, Social Security).
Performance Skills
Students will use their knowledge and skill learned throughout the Entrepreneurship course to complete one of the following:
-
Create a business/promotion plan (FBLA and/or DECA).
-
Create an innovation plan.
-
Social entrepreneurship project.
-
Create and share a presentation of how you or your team met the Entrepreneurship Performance Objective.
Workplace Skills
Students will connect their knowledge with current workplace skills including:


 UTAH EDUCATION NETWORK
UTAH EDUCATION NETWORK

 Justin
Justin Braxton
Braxton Dani
Dani Kayla
Kayla Katie
Katie Lora
Lora Rob
Rob Val
Val
